Subscribe YouTube Channel For More Live Tutorials
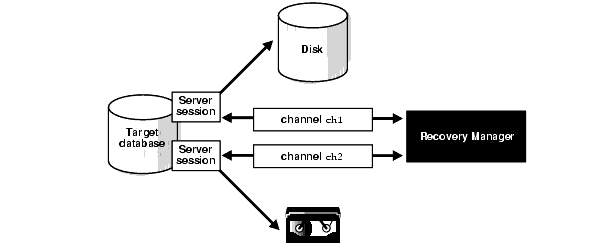
An RMAN channel represents one stream of data to a device type and corresponds to one server session.
Allocation of one or more RMAN channels is necessary to execute most backup and recovery commands.
Each channel establishes a connection from the RMAN executable to a target or auxiliary database instance by starting a server session on the instance.
The server session performs the backup, restore, and recovery operations.
Only one RMAN session communicates with the allocated server sessions.
RMAN Channels – How it works
You can either allocate channels manually within a RUN block, or preconfigure channels for use in all RMAN sessions using automatic channel allocation. RMAN comes preconfigured with a DISK channel that you can use for backups and copies to disk. You can also run the CONFIGURE CHANNEL command RMAN to specify automatic channels to disk or tape. In this way, you do not have to allocate channels every time you perform a backup, restore, or recovery operation.
When you run a command that requires a channel, and you do not allocate a channel manually, then RMAN automatically allocates the channels using the options specified in the CONFIGURE command. For the BACKUP command, RMAN allocates only a single type of channel, such as DISK or sbt. For the RESTORE command and the various maintenance commands (for example, DELETE), RMAN determines which device types are required, and allocates all necessary channels.
If you specify channels manually, then the ALLOCATE CHANNEL command (executed only within a RUN command) and ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE command (executed only at the RMAN prompt) specify the type of I/O device that the server session will use to perform the backup, restore, or maintenance operation.
Whether the ALLOCATE CHANNEL command or CONFIGURE CHANNEL causes the media manager to allocate resources is vendor-specific. Some media managers allocate resources when you issue the command; others do not allocate resources until you open a file for reading or writing.
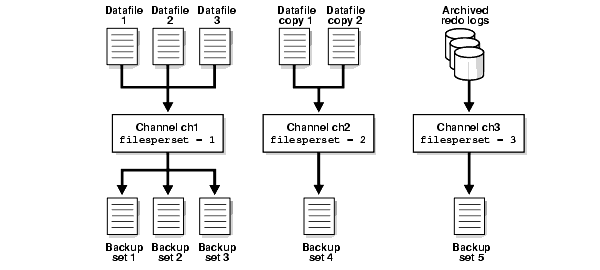
Parallelization of Backups